Failure Analyses of Mechanical and Structural Components

Whenever practical, analytical predictions should be performed in concert with failure analyses to completely understand and successfully diagnose problems associated with the operation of rotating equipment. Over the years, PARSTURBO has provided its customers with failure analysis support to address existing problems. In addition to using our own eyes, we routinely utilize both light and electron microscopy to facilitate our evaluations. When needed, we can arrange for specialized testing such as: material mechanical strength and fatigue, dimensional verification, and lubricant analysis.
Failure analysis serves to determine remedial actions, or design improvements, to prevent recurrence of failure after replacement (or repair) of failed equipment, and thus the prevention of further undesirable safety and economic consequences.
Failure analysis can provide impartial and consistent diagnoses of the sequence of damage. This capacity is typically required when you need to confirm whether failure was induced by equipment service history or by manufacturing defects.
Typical Problem Areas:
- Weld joint failures of pressure equipment; e.g. pressure vessels, piping, and headers
- Weld joint failures of dynamically loaded structures; e.g. towers, lifting equipment
- Shaft and bearing failures of rotating equipment
- Tube and header failures in boilers and heat recovery units
- Failures of gas and steam turbine components
- Failures of heavy duty equipment in mining industry; e.g. joy miner and conveyors
- Failures of hydrogen containing pressure vessels
- Corrosion damage of structures and piping
Failure Assessment of the First Stage Blade of a Gas Turbine Engine
Abstract

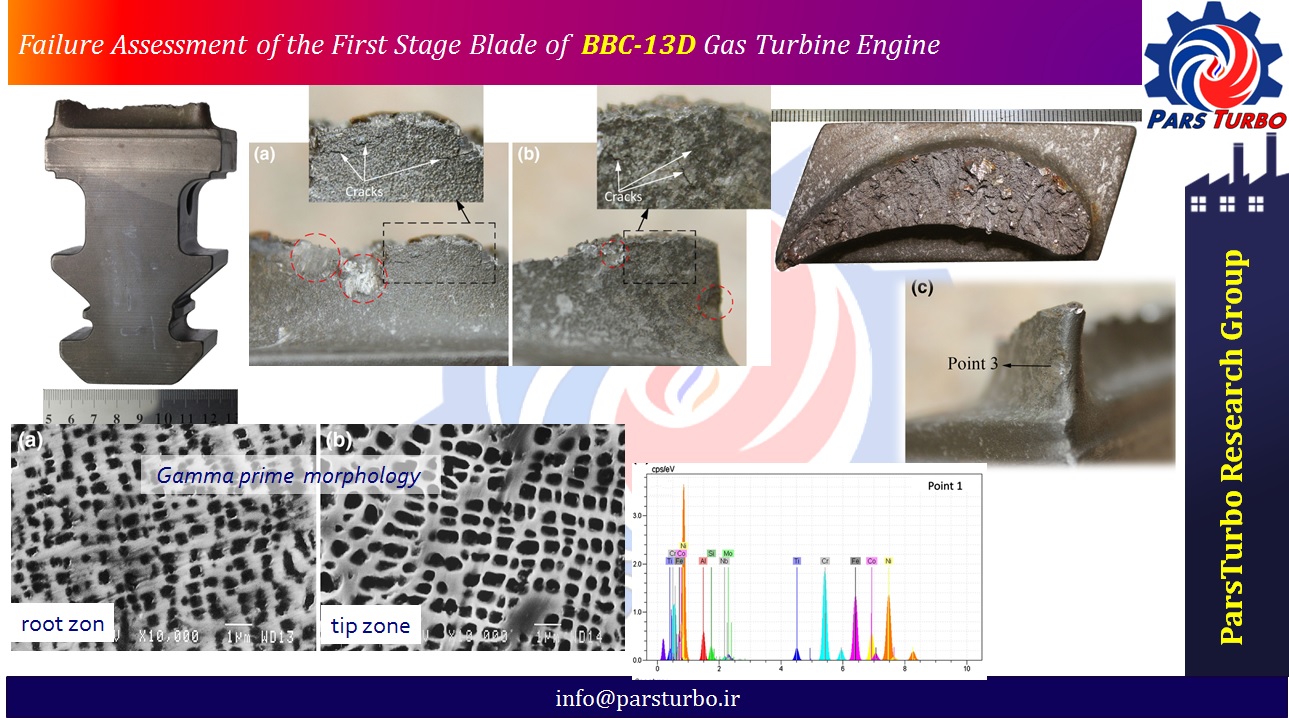
The gas turbine engine under investigation in this paper was in service after major overhaul for about 2 h at 9:47 A.M. on 18 October, 2014. The 60 MW gas turbine engine experienced a forced break down because of extremely high vibrations and subsequent output power reduction. The blade was made of Inconel 738LC nickel-based super-alloy. Evaluation of the microstructures of the root and tip of the damaged blade, showed no significant change in the microstructure. In closer observation of the fractured blade, some points affected by impact of the remaining airfoil were observed. Metallurgical investigations of the damaged zones of the fractured blade showed many iron rich zones near the fractured surface. The morphology of the fractured surface showed a semi-brittle fracture due to the impact. Finally, it was concluded that the main reason for the gas turbine failure was domestic object damage due to the impact of the liberated components of the turbine engine on the blades.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs12666-016-1031-4